TBA: a Transcription Factor Binding Analysis
Published:
TBA is a multi-functional machine learning tool for identifying transcription factors associated with genomic features. Specifically, TBA can be applied to:
- ChIP-seq targeting a transcription to identify collaborative binding partners for a given transcription factor.
- DNAse-seq and ATAC-seq to identify transcription factors associated with open chromatin
- GRO-seq and other assays measuring enhancer activity to identify transcription factors associated with enhancer activty
- Predict the effect of genetic variation in any of the above contexts.
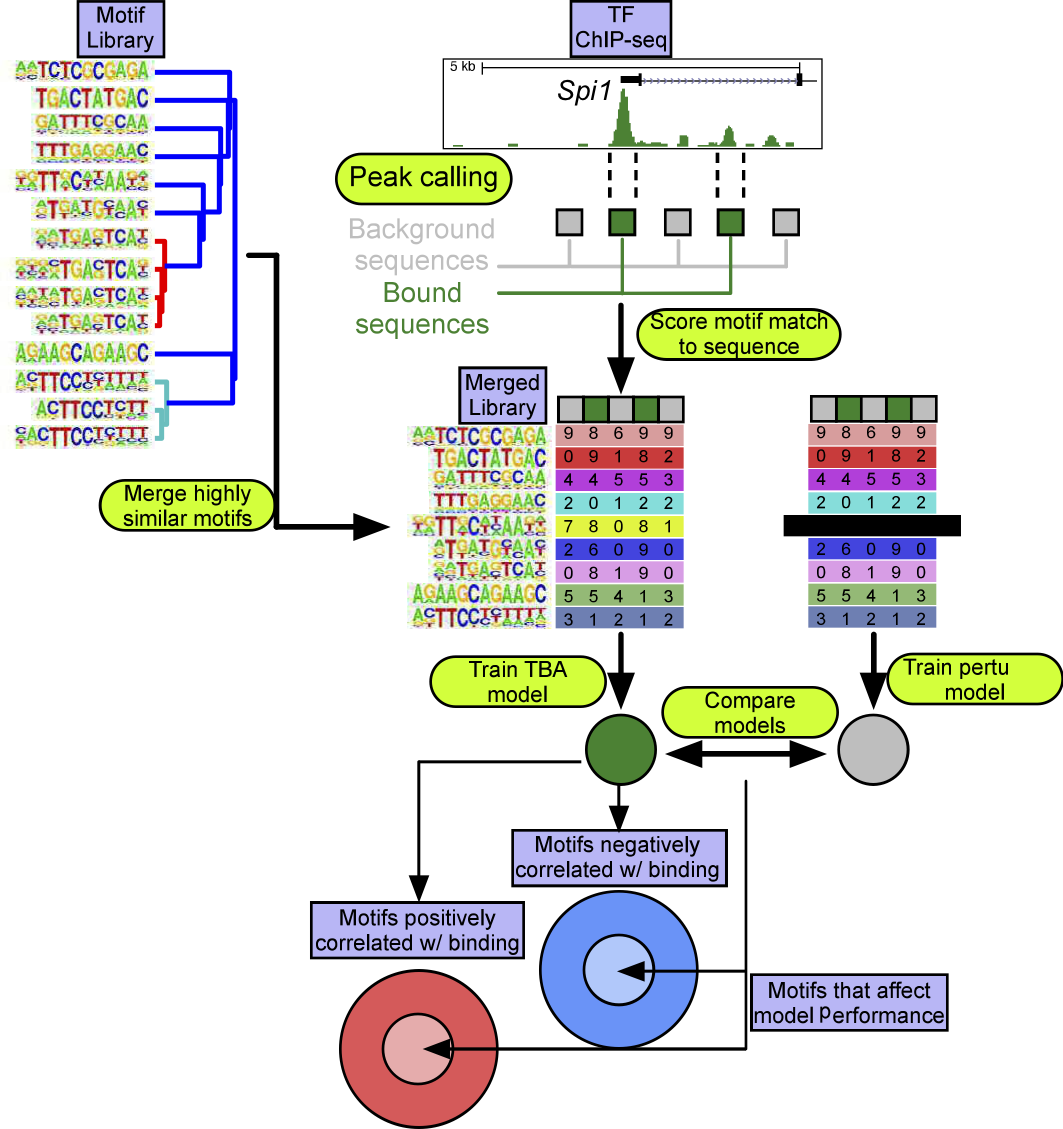
TBA takes a set of loci that are of interest as input. First, the genomic sequence of each loci of interest are retrieved. Next, TBA selects a set of GC-matched background loci. For each locus of interest and background locus, TBA calculates the best match to hundreds of DNA binding motifs, and quantifies the quality of the match as the motif score (aka log likelihood ratio score). To allow for degenerate motifs, all motif matches scoring over zero are considered. The motif scores are then used to train the TBA model to distinguish loci of interest from background loci. TBA scores the probability of observing binding at a sequence by computing a weighted sum over all the motif scores for that sequence. The weight for each motif is learned by iteratively modifying the weights until the model’s ability to differentiate binding sites from background loci no longer improves. The final motif weight measures whether the presence of a motif is correlated with TF binding.
TBA is available at github.com/jenhantao/tba